Choosing segments or segments from a Pandas DataFrame is perhaps the most habitually performed task while controlling information. Pandas give a few procedures to proficiently recover subsets of information from your DataFrame. The Python ordering administrators ‘[]’ and quality administrator ‘.’ permits basic and quick admittance to DataFrame across a wide scope of utilization cases. Following article will examine various ways of working with a DataFrame that has an enormous number of segments.
Numerous segment choice is one of the most well-known and straightforward errands one can perform. In the present short aide, we will examine a couple of potential ways for choosing various segments from a pandas DataFrame. In particular, we will investigate how to do as such
- utilizing basing ordering
- with loc
- utilizing iloc
- through the formation of another DataFrame
Furthermore, we will examine when to utilize one strategy over the other, in light of your particular use-case and regardless of whether you want to create a view or a duplicate of the first DataFrame object.
There are three basic methods you can use to select multiple columns of a pandas DataFrame:
Method #1: Basic Method
Given a dictionary which contains Employee entity as keys and list of those entity as values.
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # select two columnsdf[['Name', 'Qualification']] |
Output:
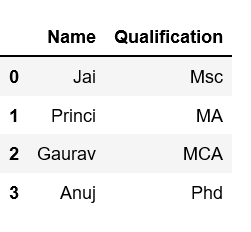
Select Second to the fourth column.
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # select all rows # and second to fourth columndf[df.columns[1:4]] |
Output:
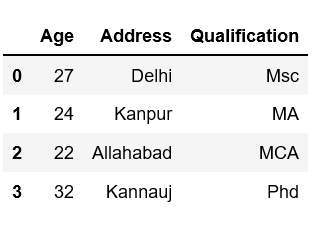
Method #2: Using loc[]
Example 1: Select two columns
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # select three rows and two columnsdf.loc[1:3, ['Name', 'Qualification']] |
Output:
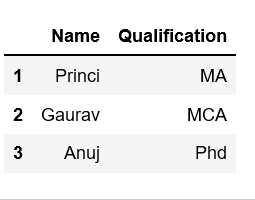
Example 2: Select one to another columns. In our case we select column name “Name” to “Address”.
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # select two rows and # column "name" to "Address"# Means total three columnsdf.loc[0:1, 'Name':'Address'] |
Output:
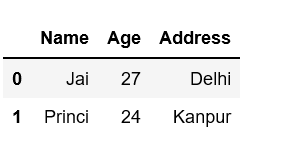
Example 3: First filtering rows and selecting columns by label format and then Select all columns.
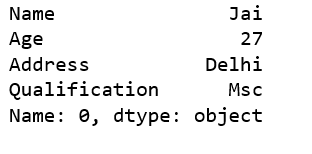
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd'] }# Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # .loc DataFrame method# filtering rows and selecting columns by label# format# df.loc[rows, columns]# row 1, all columnsdf.loc[0, :] |
Output:
Method #3: Using iloc[]
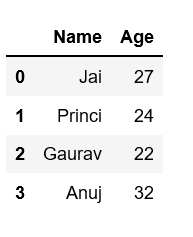
Example 1: Select first two column.
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # Remember that Python does not# slice inclusive of the ending index.# select all rows # select first two columndf.iloc[:, 0:2] |
Output:
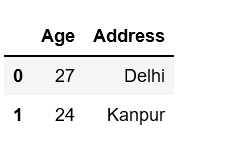
Example 2: Select all or some columns, one to another using .iloc.
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # iloc[row slicing, column slicing]df.iloc [0:2, 1:3] |
Output:
Method #4: Using .ix
Select all or some columns, one to another using .ix.
# Import pandas packageimport pandas as pd # Define a dictionary containing employee datadata = {'Name':['Jai', 'Princi', 'Gaurav', 'Anuj'], 'Age':[27, 24, 22, 32], 'Address':['Delhi', 'Kanpur', 'Allahabad', 'Kannauj'], 'Qualification':['Msc', 'MA', 'MCA', 'Phd']} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(data) # select all rows and 0 to 2 columns print(df.ix[:, 0:2]) |
Output:

Method 1: Select Columns by Index
df_new = df.iloc[:, [0,1,3]]
Method 2: Select Columns in Index Range
df_new = df.iloc[:, 0:3]
Method 3: Select Columns by Name
df_new = df[['col1', 'col2']]
The following examples show how to use each method with the following pandas DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
#create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'points': [25, 12, 15, 14, 19, 23, 25, 29],
'assists': [5, 7, 7, 9, 12, 9, 9, 4],
'rebounds': [11, 8, 10, 6, 6, 5, 9, 12],
'blocks': [4, 7, 7, 6, 5, 8, 9, 10]})
#view DataFrame
df
points assists rebounds blocks
0 25 5 11 4
1 12 7 8 7
2 15 7 10 7
3 14 9 6 6
4 19 12 6 5
5 23 9 5 8
6 25 9 9 9
7 29 4 12 10
Method 1: Select Columns by Index
The following code shows how to select columns in index positions 0, 1, and 3:
#select columns in index positions 0, 1, and 3
df_new = df.iloc[:, [0,1,3]]
#view new DataFrame
df_new
points assists blocks
0 25 5 4
1 12 7 7
2 15 7 7
3 14 9 6
4 19 12 5
5 23 9 8
6 25 9 9
7 29 4 10
Notice that the columns in index positions 0, 1, and 3 are selected.
Note: The first column in a pandas DataFrame is located in position 0.
Method 2: Select Columns in Index Range
The following code shows how to select columns in the index range 0 to 3:
#select columns in index range 0 to 3
df_new = df.iloc[:, 0:3]
#view new DataFrame
df_new
points assists rebounds
0 25 5 11
1 12 7 8
2 15 7 10
3 14 9 6
4 19 12 6
5 23 9 5
6 25 9 9
7 29 4 12
Note that the column located in the last value in the range (3) will not be included in the output.
Method 3: Select Columns by Name
The following code shows how to select columns by name:
#select columns called 'points' and 'blocks'
df_new = df[['points', 'blocks']]
#view new DataFrame
df_new
points blocks
0 25 4
1 12 7
2 15 7
3 14 6
4 19 5
5 23 8
6 25 9
7 29 10
Also Read: How to drop one or multiple columns in Pandas Dataframe